
The concept of a circular economy has gained significant traction in recent years as societies grapple with the environmental and social consequences of traditional linear economic models. Unlike the linear “take, make, dispose” approach, a circular economy seeks to minimize waste and make the most of resources by fostering a closed-loop system. In this article, we will explore what a circular economy entails, its benefits for society and the planet, certifications that signify commitment to circular principles, and how both consumers and businesses can actively participate in and promote this sustainable model.
Understanding the Circular Economy

The circular economy operates as a system in which materials avoid becoming waste, and the natural environment is revitalized. Within this framework, products and materials are sustained in a continuous loop through practices such as maintenance, reuse, refurbishment, remanufacture, recycling, and composting. By decoupling economic activity from the consumption of finite resources, the circular economy addresses pressing global issues such as climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution.
This approach challenges the traditional linear economy, where products have a finite life cycle, leading to resource depletion and environmental degradation. In contrast, a circular economy seeks to create a regenerative system where materials are reused and repurposed, reducing the overall environmental impact.
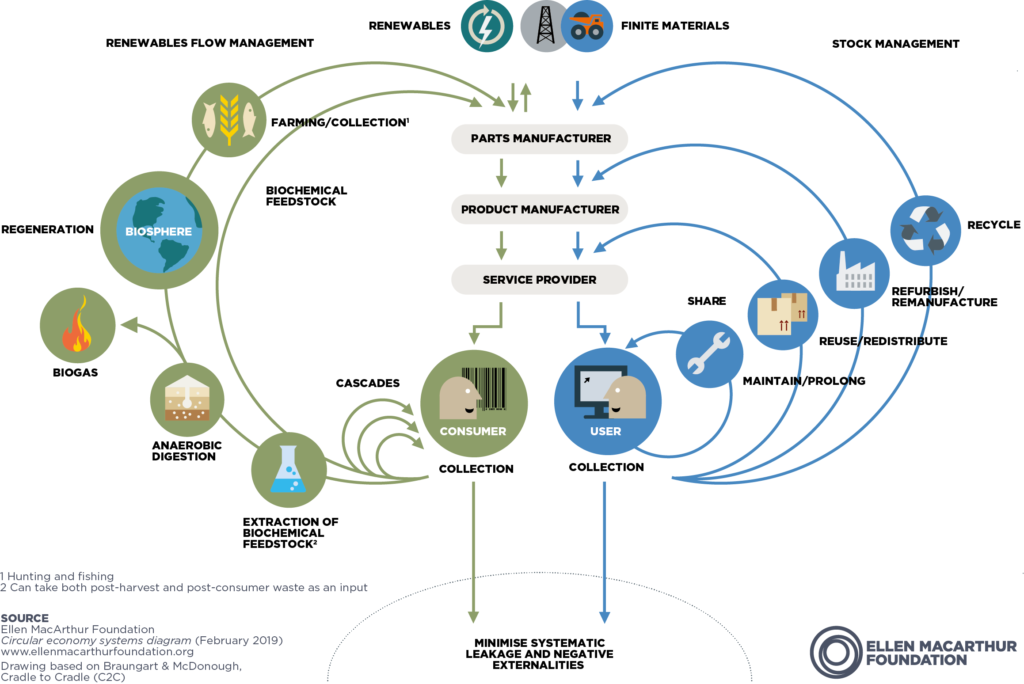
The butterfly diagram, a representation of the circular economy system, delineates the uninterrupted movement of materials within this sustainable model. It comprises two primary cycles: the technical cycle and the biological cycle. In the technical cycle, products and materials are sustained in circulation through activities like reuse, repair, remanufacture, and recycling. Meanwhile, the biological cycle involves the return of nutrients from biodegradable materials to the Earth, contributing to the regeneration of the natural environment.
Benefits for Society and the Planet
- Resource Conservation: A circular economy minimizes the extraction of finite resources, promoting sustainable practices that contribute to the preservation of ecosystems.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By minimizing waste and emissions, a circular economy helps mitigate pollution and climate change, fostering a healthier planet for future generations.
- Job Creation: The shift towards a circular economy requires new skills and jobs, fostering economic growth in industries focused on recycling, remanufacturing, and sustainable practices.
Certifications for Circular Economy Products
Consumers play a crucial role in driving the demand for sustainable products. Various certifications help them identify items that adhere to circular principles. Notable certifications include:
Cradle to Cradle (C2C): This certification evaluates products based on their material health, material reutilization, renewable energy use, water stewardship, and social responsibility, providing a comprehensive view of a product’s sustainability. To obtain certification, businesses are required to undergo the demanding certification process overseen by the Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute.
Certification entails meeting specific criteria and adhering to standards such as ensuring the safety of materials for both humans and the environment, facilitating a circular economy through the design of regenerative products and processes, advocating for clean air, endorsing renewable energy, and minimizing harmful emissions. Additionally, companies must also prioritize the protection of clean water, the promotion of healthy soils, and uphold human rights while contributing to a fair and equitable society.
The Cradle to Cradle certification offers various recognition levels, namely Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Each level signifies a distinct degree of dedication to environmental sustainability.
EU Ecolabel: Recognized across Europe, this label signifies that a product or service meets strict environmental performance criteria throughout its life cycle. It is a voluntary program that advocates for products and services showcasing environmental excellence through standardized procedures and scientific proof. It is independently verified by third-party experts who assess adherence to the EU Ecolabel criteria. Currently, 88,921 products (goods and services) have received the EU Ecolabel certification. These awarded products comply with strict criteria for reducing their environmental impact, from the extraction of raw materials to distribution and end-of-life.
Participating in the Circular Economy
- Smart Consumption: Consumers can make a significant impact by choosing products with circular certifications, promoting a market demand for sustainable goods.
- Extended Product Life: Repair, reuse, and recycle whenever possible to extend the lifespan of products and reduce the need for constant replacements.
- Support Circular Businesses: Choose to support businesses committed to circular principles, encouraging others to follow suit by creating demand for sustainable practices.
- Increase your knowledge: You can do an online course through The Ellen MacArthur Foundation. There are variety of courses, all aimed at ensuring consumers understand its origin, design, and importance for the planet and our economy, and businesses understand those ideas, plus how they can implement the required changes.
Encouraging Companies to Embrace the Circular Economy
- Consumer Advocacy: Actively engage with companies through social media, expressing support for circular initiatives and urging them to adopt sustainable practices.
- Educate and Raise Awareness: Share information about the circular economy’s benefits with your network, encouraging others to make informed choices and support sustainable businesses.
- Lobby for Policy Change: Advocate for policies that incentivize circular practices and penalize wasteful activities, fostering a regulatory environment conducive to sustainable business practices.
The transition to a circular economy represents a pivotal step towards a sustainable and regenerative future. As consumers, businesses, and governments collectively embrace circular principles, we can create a world where economic growth is decoupled from resource depletion, benefitting both society and the planet. By making informed choices and actively supporting circular initiatives, each individual becomes a catalyst for positive change, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient global economy.


